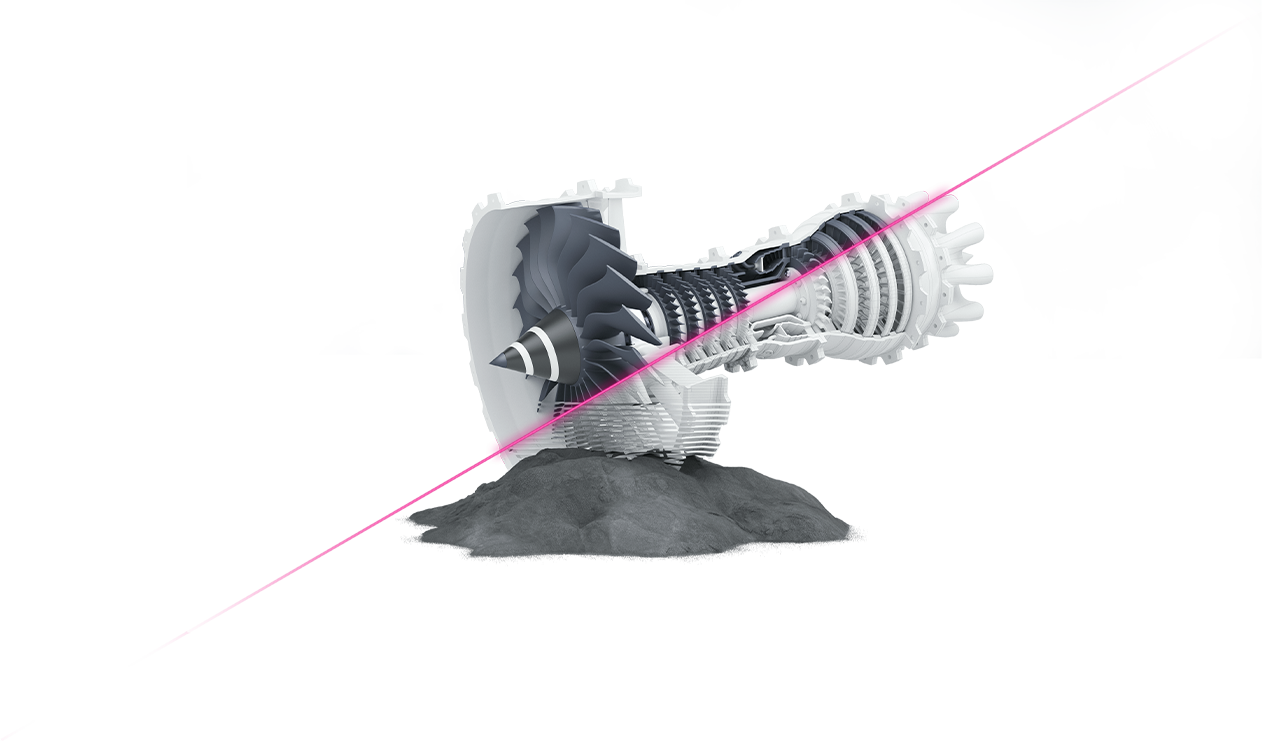
Industrial 3D printing
“Come to stay”. 3D printing has become part of everyday life for millions of people. Hearing aids, dentures, spare and wear parts very often come from 3D printers.
The technology can be found in gas turbines, aircraft engines – and even in Rolls-Royces. For years, brackets for hazard warning lights, parking brakes and sockets in the luxury saloon have been produced as standard in 3D printers and installed between fine burl wood and leather seats.
WESTCAM is rightly proud of more than two decades of experience in additive manufacturing. We provide you with reliable advice on which processes and industrial 3D printers are best suited to your requirements.
WE RECOMMEND: TEST FIRST, THEN BUY
Investing in a professional 3D printer needs to be carefully considered and must also pay for itself within a reasonable period of time(ROI). No stress! Put us and the best 3D printing process for you through its paces before you buy your own system. Thanks to our comprehensive 3D printing services, you have the opportunity to secure your investment decision to a sufficient extent in advance.
- Distribution of professional 3D printers & consumables
- Support in selecting the right process for your application
- Ongoing maintenance and service
- Printing and modeling your components
- Further training and product training in the field of 3D printing and design
- Component optimization
What you always wanted to know about 3D printing
What is 3D printing?
3D printing is also known as 3D printing, additive manufacturing or rapid prototyping.
This refers to the production of three-dimensional objects, usually by applying material layer by layer. As the individual layers adhere to each other, the object becomes higher each time, giving it its 3D character.
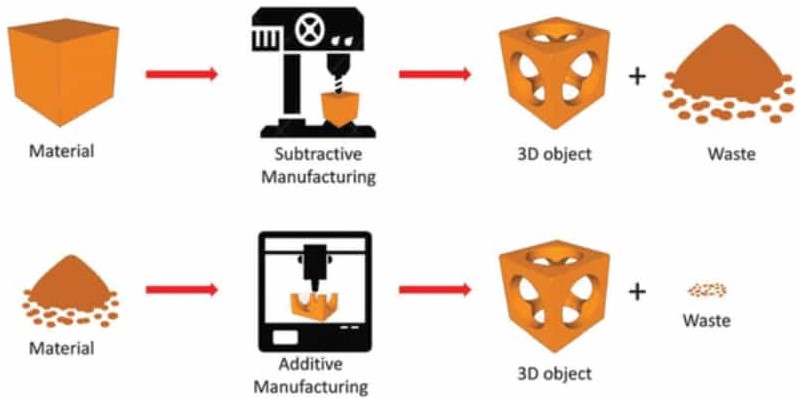
Additive manufacturing vs. subtractive manufacturing
In contrast to additive manufacturing, subtractive manufacturing removes material from a larger starting block or blank to achieve the desired shape.
Common subtractive processes include milling, turning, eroding, drilling and grinding. CNC (Computerized Numerical Control) technology enables machines to precisely process materials such as metal, plastic, wood and composites.
What are 3D printers used for?
3D printers have long been more than just a gimmick. Whether medical and hearing aid technology, aerospace or automotive – we encounter additive manufacturing everywhere these days. 3D printing has long since found its way into industrial production.
More and more private individuals are also using 3D technology. Hobbyists in the DIY sector or in model making as well as craftsmen. For example, special tools are produced. Or quickly and easily producing spare parts for broken objects. However, these target groups generally use different devices than industry.

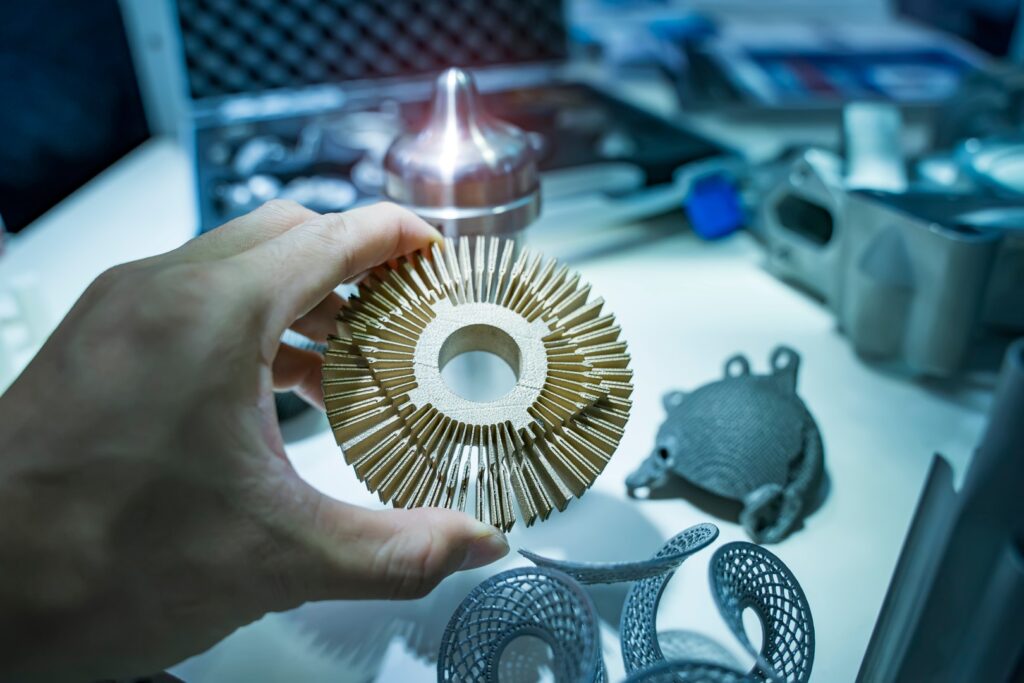
3D printers for private use vs. industrial applications
Depending on the requirements, 3D printers differ greatly in terms of suitable processes and therefore also in terms of price.
3D printers for private use are available from just a few hundred euros to around a thousand euros. Industrial systems, which are subject to strict quality standards, are correspondingly more expensive but also more powerful.
For those who do not need 3D printers on a regular basis, we recommend having the objects printed by external service providers instead of buying a device . WESTCAM offers precisely this service in a reliable and professional manner:
Which 3D printers are available?
There are various 3D printers, each of which uses different processes and materials (e.g. plastic, metal, sand casting).
Not every printer and every process is equally suitable for every 3D object. When making a selection, the desired size, quality and material of the 3D object to be created must be taken into account. There are also major differences in price between the individual devices and processes.

3D printers for industrial use
3D printers designed for industrial use can be easily differentiated according to the materials used:
3D printing of metal components
3D metal printing is used to manufacture tools or robust housings , among other things. The materials often used are aluminum, stainless steel or titanium . You can find out more about 3D metal printing here: Metal – Laser and Metal – Electon Beam Melting
3D printing of plastic and plastic-like components
This type of 3D printing uses powdered plastic or resins as the material. A distinction is made between the additive processes of selective laser sintering and stereolithography or digital light plotting. For more information, see our overview pages on the ETEC portfolio and Voxeljet portfolio
Sand casting 3D printing
In sand casting 3D printing technology, sand molds are made from fine quartz sand. These are used, for example, for grey and steel casting and for the production of castable metals such as aluminum, brass or magnesium. In addition to prototype or tool production, sand casting molds from the 3D printer are also used for the production of designer furniture, for restorations, in architecture and in the aerospace industry. More details about sand casting 3D printing can be found in this portfolio overview.
3D printing software
How does the 3D printer actually know what to print? That’s where the 3D printing software comes in – a small but important detail. It transmits all the information relevant to the print to the printer. Which software do we recommend for industrial 3D printing? Take a look at our overview:
Overwhelmed with so much choice? Get THE advice of our experts!
The technologies are just as diverse as the areas of application for 3D printing. With the sheer endless choice of 3D printers, it’s easy to lose track. It’s good to have a partner at your side who knows what to look out for and where the opportunities and risks of various processes and materials lie.
WESTCAM offers sophisticated industrial solutions for 3D printers and 3D printing software. Whether metal, plastic or sand printing – you are in the best hands with us! Guaranteed!
